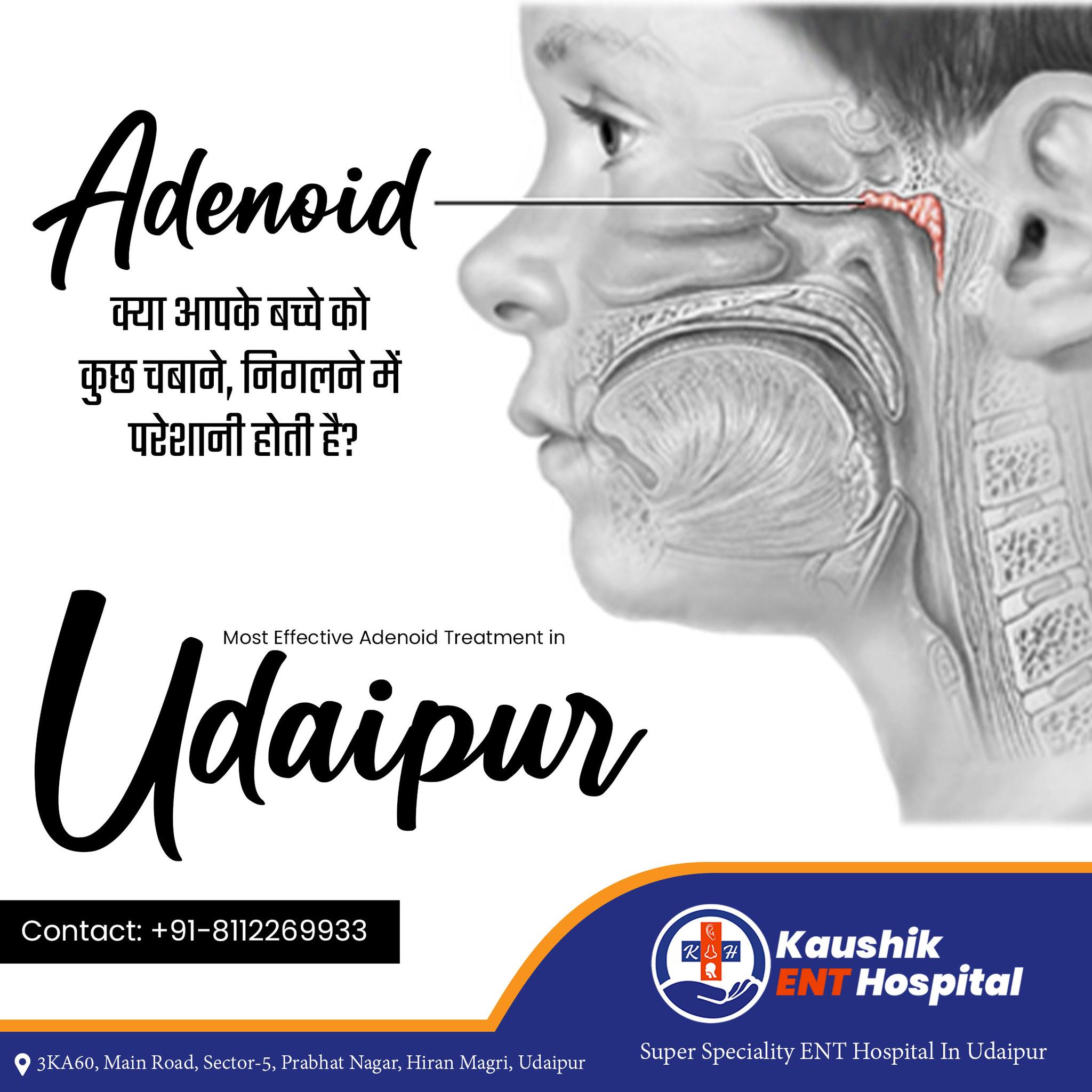
The adenoids are lymph tissues that sit in your upper airway between your nose and the back of your throat. They are similar to the tonsils. Enlarged adenoids means this tissue is swollen. Enlarged adenoids may be normal. They may grow bigger when the baby grows in the womb. The adenoids help the body prevent or fight infections by trapping bacteria and germs.
What is an Adenoid?
The adenoid is a structure located at the junction of the nose and throat (nasopharynx) that functions in the immune system. Although it is beneficial, issues may occur with the adenoid. The adenoid physiologically enlarges during childhood around ages 2-4 years (although an enlarged adenoid may present in children younger than 1 year of age) and the increased size may cause problems.
What Problems May Result from an Enlarged Adenoid?
An enlarged adenoid may cause snoring, mouth breathing, persistent congestion, nasal drainage, ear problems, sinusitis, and “nasal” voice quality (the way you sound when you have a cold). Many of these symptoms can be transient; however, persistence of the aforementioned may necessitate evaluation by an Otolaryngologist or ENT specialist.
How Are the Adenoids Evaluated?
The adenoid is not visible without the aid of a fiberoptic endoscope or use of an X-ray. An ENT specialist will evaluate your child by performing a flexible nasopharyngoscopy in your child’s nose to determine if the adenoid is contributing to the problem.

Adenoidectomy in Udaipur | Adenoid Removal Surgery in Udaipur | Adenoid Treatment in Udaipur
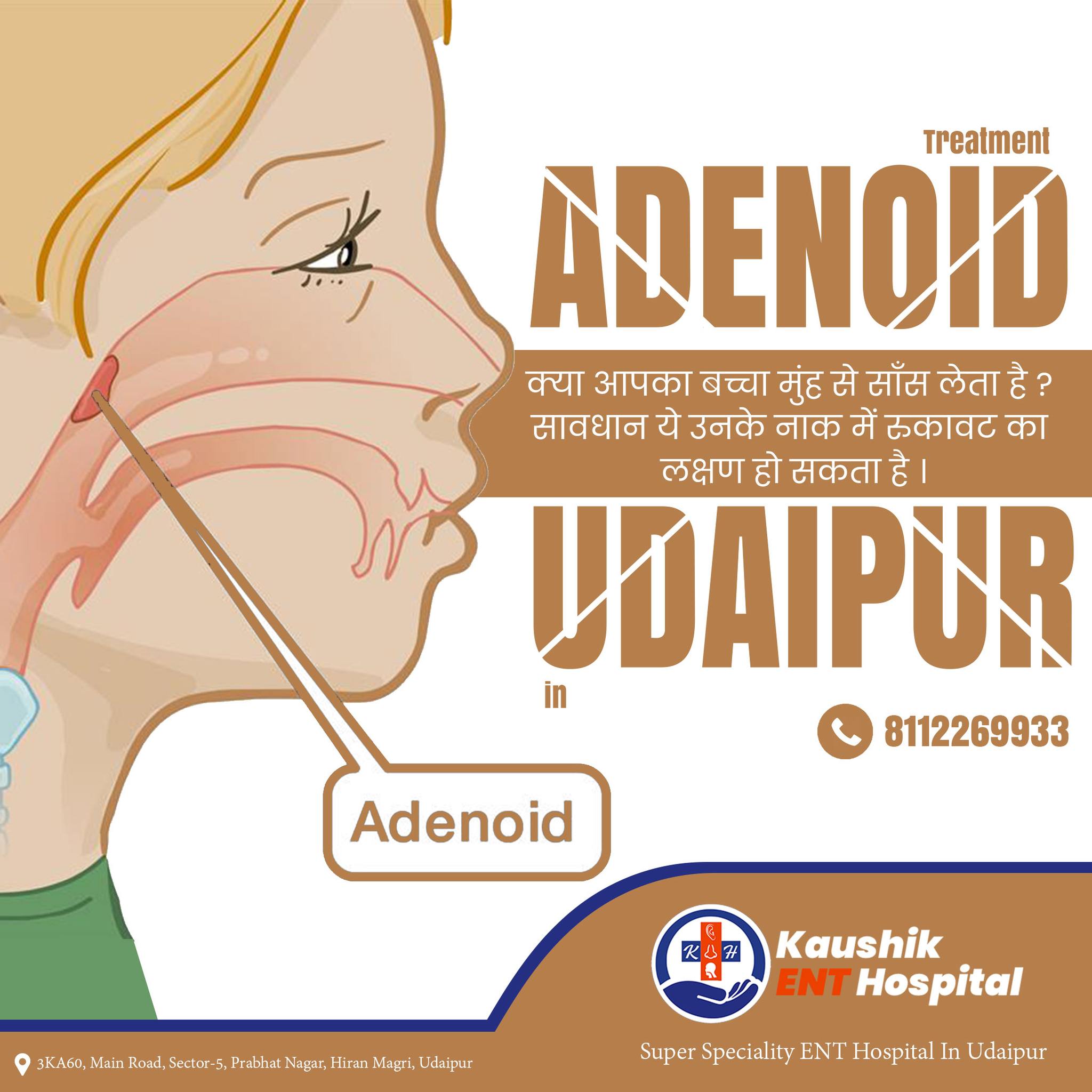
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of Enlarged Adenoids?
Kids with enlarged adenoids might:
- have trouble breathing through the nose
- breathe through the mouth (which can lead to dry lips and mouth)
- talk as if the nostrils are pinched
- have noisy breathing (“Darth Vader” breathing)
- have bad breath
- snore
- stop breathing for a few seconds during sleep (obstructive sleep apnea), which can lead to disturbed sleep. This in turn can cause learning, behavioral, growth, and heart problems, and sometimes bedwetting.
- have frequent or chronic (long-lasting) nose or sinus infections
- have ear infections, middle ear fluid, and hearing loss
Enlarged Adenoid Symptoms
What Is an Adenoidectomy?
An adenoidectomy is the surgical removal of the adenoids. It’s one of the most common surgical procedures done on children, along with the removal of tonsils.
If swollen adenoids bother your child and don’t respond to medicine, a health care provider may recommend an adenoidectomy.
What Happens During the Adenoidectomy?
What Happens During the Adenoidectomy?
An ENT surgeon will do the surgery in an operating room. Your child will get general anesthesia. This means an anesthesiologist will carefully watch your child and keep him or her safely and comfortably asleep during the procedure. The surgery is done through your child’s open mouth — there are no cuts through the skin and no visible scars.
What Happens After the Adenoidectomy?
Your child will wake up in the recovery area. In most cases, kids can go home the same day as the procedure. Some may need to stay overnight for observation.
The typical recovery after an adenoidectomy often involves a few days of mild pain and discomfort, which may include sore throat, runny nose, noisy breathing, or bad breath.
In less than a week after surgery, everything should return to normal and the problems caused by the adenoids should be gone. There are no stitches to worry about, and the adenoid area will heal on its own.






Leave A Comment