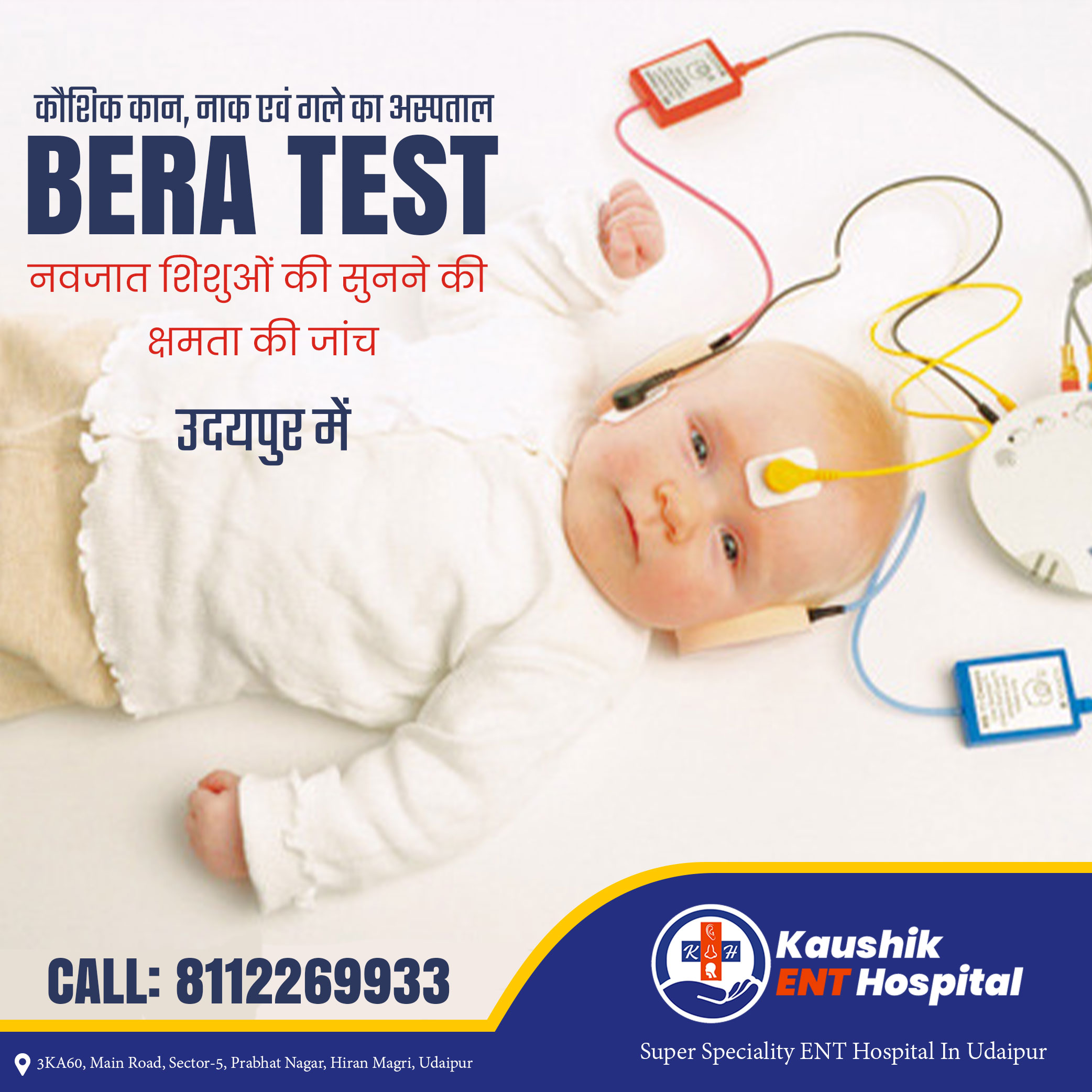
What is BERA Test?
Brain Evoked Response Auditory (BERA) is a hearing examination performed on children aged 1 to 3 years. Meanwhile, for children with a smaller age, Oto Acoustic Emission (OAE) examination can be carried out. If the BERA test results are stated in good condition, it can be concluded that the child’s hearing function is within normal limits and no further medical treatment is necessary. However, if the BERA test results are declared abnormal, then the examination will continue with the estimation or prediction of the hearing threshold and hearing rehabilitation must be carried out as early as possible by using hearing aids. BERA test itself will take approximately one hour.
Why do the BERA Test?
Hearing loss in children is difficult to know from the beginning. Hearing loss can cause speech, language, cognitive, social and emotional problems. Therefore, it will be better if the hearing test in children is done early.
Healthy hearing is when the auditory nerve is able to transmit sound impulses from the ear to the brain at a certain speed. The BERA test can provide information on whether nerves convey sound impulses to the brain and whether the speed of sound delivery is within normal limits. This hearing examination can determine the type of abnormality (conductive or sensorineural), severity (hearing threshold), and hearing loss (inner ear or other parts) of the child.
In addition, in determining the hearing threshold, BERA is also used in otoneurologic diagnosis. This is useful for patients with unilateral or asymmetrical hearing loss (hearing nerve tumors, brain tumors, other nerve disorders, multiple sclerosis, etc.).
BERA Test Procedure
BERA can be done without the patient needing to do anything. Patients only need to lie down and preferably in a calm attitude or while sleeping. For children, this examination can be done in the wake, sleep, or in anesthesia (although rarely). Electrodes will be placed on the patient’s head and behind the ear during the BERA test procedure. When the examination is done, the patient will be heard various sounds through headphones. This examination measures changes in brain electrical activity (EEG) in the provision of acoustic stimuli. Abnormalities that occur in the transmission of signals when the sound is heard indicates hearing loss.
This examination has no risk of complications, is painless, and does not require special preparation for the BERA test.
What is OAE Test
Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE) Testing
The OAE (Otoacoustic Emissions) test checks part of the inner ear’s response to sound. The test is mostly done on infants and children who may not be able to respond to behavioral hearing tests because of their age.
What are Otoacoustic Emissions?
Otoacoustic Emissions are sounds given off by one small part of the cochlea when it is stimulated by soft clicking sounds. When the sound stimulates the cochlea, the outer hair cells vibrate. The vibration produces a nearly inaudible sound that echoes back into the middle ear.
How is the OAE test done?
Soft foam or rubber tips are placed in your child’s ear. Your child will hear soft sounds through the soft foam or rubber tips. A computer will record quiet echoes from the ear.
How should I prepare for the test?
Your child is not required to sleep during this test. However, for this test, your child, and everyone in the room, must be able to sit still and be very quiet. Your child will not feel anything during this test.
How long is the OAE test?
This test should only take a few minutes.
What do the results mean?
The results are either present or absent.
- Present OAEs are consistent with normal to near normal hearing.
- Absent OAEs may be a sign of a problem. It could be hearing loss, wax in the ears, fluid or infection in the middle ear or a malformed inner ear. This indicates that more testing needs to find out why the OAEs were absent, and to rule out any possible hearing loss.






Leave A Comment